Thermal runaway happens when a lithium-ion cell, or a small region within a cell, reaches a critical temperature where the materials start to undergo decomposition reactions. These reactions then generate significant additional heat. The decomposition reactions are temperature dependent, increasing exponentially as the temperature increases. Once decomposition starts, a chain reaction causes the battery to…
EV battery technologies: From the state of the art to the future energy stores
Lithium-ion batteries have significantly increased the capability of electric vehicles, with high energy storage density and efficiency. They can currently achieve specific energy and power densities of 260 Wh/kg and 340 W/kg, respectively, with a life of over 1,000 cycles. In recent years, most developments in lithium-ion batteries have focused on cathode chemistry, with battery…
What to consider when evaluating battery performance
Several important metrics and considerations are important when evaluating battery performance: Cell, module, and pack level: It is important to consider whether the data refers to an individual cell or a complete battery pack when comparing energy and power densities. Cells will always have the highest energy and power for a given size or weight.…
Comparing EV battery and fuel cell energy density
Battery electric vehicles (BEV) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV) are two “zero-emissions” vehicles. Although none achieve zero emissions, as discussed below. The amount of energy stored in a battery or hydrogen tank for a FCEV can be measured in two ways: Energy Density: Energy per unit volume, also known as volumetric energy density Specific…
How electric vehicle wireless charging works
Wireless charging allows an electric vehicle to be charged simply by parking it over a wireless charging pad containing an electrical coil. Vehicles can even be charged dynamically while driving along roads having multiple embedded coils. This works using the same principle as wireless phone charging or a transformer – electromagnetic induction. Induction is the…
Lithium-ion battery chemistries
Lithium-ion batteries are a popular type of rechargeable battery which stores energy in lithium ions. They typically have a lithium metal oxide cathode and a graphite anode, separated by a thin layer of lithium salt solution acting as the electrolyte. Different battery chemistries use different cathode, anode, and electrolyte materials to change the battery’s performance.…
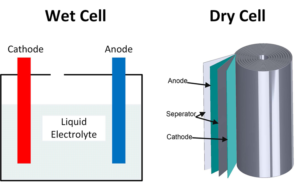
Dry cell vs wet cell batteries
Wet cell batteries have a pool of liquid electrolytes; they generate gases meaning they require venting and must be kept upright to avoid leakage. Dry cell batteries use paste electrolytes, which contain enough liquid for good electrical conductivity, but are stable enough not to leak when turned upside down. The first batteries were wet cells…
What is cell potential?
In simple terms, cell potential is the voltage of a single electrochemical cell. A battery may package a number of cells in series in order to increase the voltage of the battery. Cell potential is inherent in a particular chemical reaction, so a fully charged lead-acid battery will always have cell potentials of approximately 2.1…
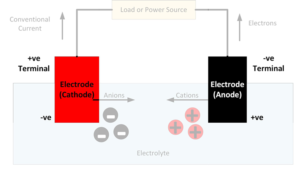
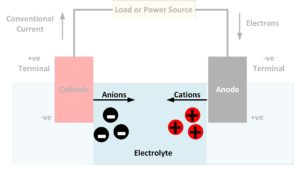
What is an electrode?
In general, an electrode is an electrical conductor which makes contact with a non-metallic part of a circuit. In a battery, the electrodes connect the battery terminals to the electrolyte. The electrode at the positive terminal is known as the cathode and the electrode at the negative terminal is known as the anode. Each electron…
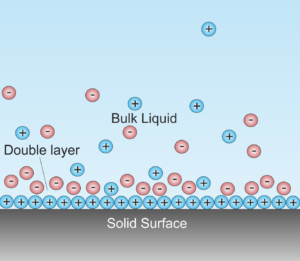
What is an electrolyte?
The electrolyte in a battery is the substance that allows electrical current to flow between the anode and the cathode. Electrolytes may be fluids or solids. Soluble salts, acids, and bases can generally act as electrolytes. While current flows through a metallic conductor in the form of lone electrons, within an electrolyte current flows in…