Battery cells, modules, and systems support many electronic, transportation, and energy applications. This article briefly reviews the operation of rechargeable batteries and looks at the energy storage value chain; it then presents common battery cell formats and how battery cells are assembled into modules and systems, reviews the development of multi-function structural battery packs, and…
EV battery technologies: From the state of the art to the future energy stores
Lithium-ion batteries have significantly increased the capability of electric vehicles, with high energy storage density and efficiency. They can currently achieve specific energy and power densities of 260 Wh/kg and 340 W/kg, respectively, with a life of over 1,000 cycles. In recent years, most developments in lithium-ion batteries have focused on cathode chemistry, with battery…
How tiny solid-state batteries enable smaller implants that recharge faster
With a solid electrolyte, high energy density and thin packaging, solid-state batteries are getting smaller and enabling devices to be implanted in more parts of the body. Denis Pasero, Ilika It has been more than six decades since Åke Senning implanted the first heart pacemaker in a patient. Even though today’s pacemakers have improved treatment…
How to choose a battery
Many embedded circuits and devices rely on batteries for a power supply and many of these devices use primary batteries that may need to be replaced. Other embedded devices are rechargeable and use secondary batteries to remain powered. It is not difficult to select a battery type, chemistry, or packaging for a given circuit or…
What to consider when evaluating battery performance
Several important metrics and considerations are important when evaluating battery performance: Cell, module, and pack level: It is important to consider whether the data refers to an individual cell or a complete battery pack when comparing energy and power densities. Cells will always have the highest energy and power for a given size or weight.…
Basics of zinc-ion batteries
By Ryan Brown, co-founder and CEO, Salient Energy Lithium-ion batteries are the leading battery technology for both electric vehicles (EVs) and the renewable energy industry. This makes it critical in the fight against climate change, with the world’s ability to adopt EVs and renewables limited in part by its ability to source lithium-ion raw materials. This…
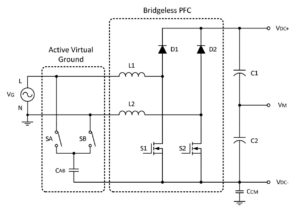
Voltage rail splitters and virtual grounds for batteries and PFCs
Rail splitters are usually associated with battery-powered devices, but that’s not always the case. There are several definitions of a “rail splitter,” sometimes referred to as a “virtual ground” or “pseudo ground.” The most common meaning is creating a new “0V” reference point, usually the mid-point Vin/2 of a single supply voltage such as a […]
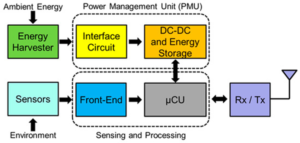
Don’t rush to choose rechargeable batteries…at least, not yet
Using energy harvesting and a rechargeable battery to power a remote wireless IoT node seems like an obvious and straightforward solution, but there are some unique aspects to consider. Don’t get me wrong: I really like rechargeable batteries; in fact, I like them a lot. Whether based on lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, lithium-ion, or other chemistry, our […]
Comparing EV battery and fuel cell energy density
Battery electric vehicles (BEV) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV) are two “zero-emissions” vehicles. Although none achieve zero emissions, as discussed below. The amount of energy stored in a battery or hydrogen tank for a FCEV can be measured in two ways: Energy Density: Energy per unit volume, also known as volumetric energy density Specific…
How electric vehicle wireless charging works
Wireless charging allows an electric vehicle to be charged simply by parking it over a wireless charging pad containing an electrical coil. Vehicles can even be charged dynamically while driving along roads having multiple embedded coils. This works using the same principle as wireless phone charging or a transformer – electromagnetic induction. Induction is the…