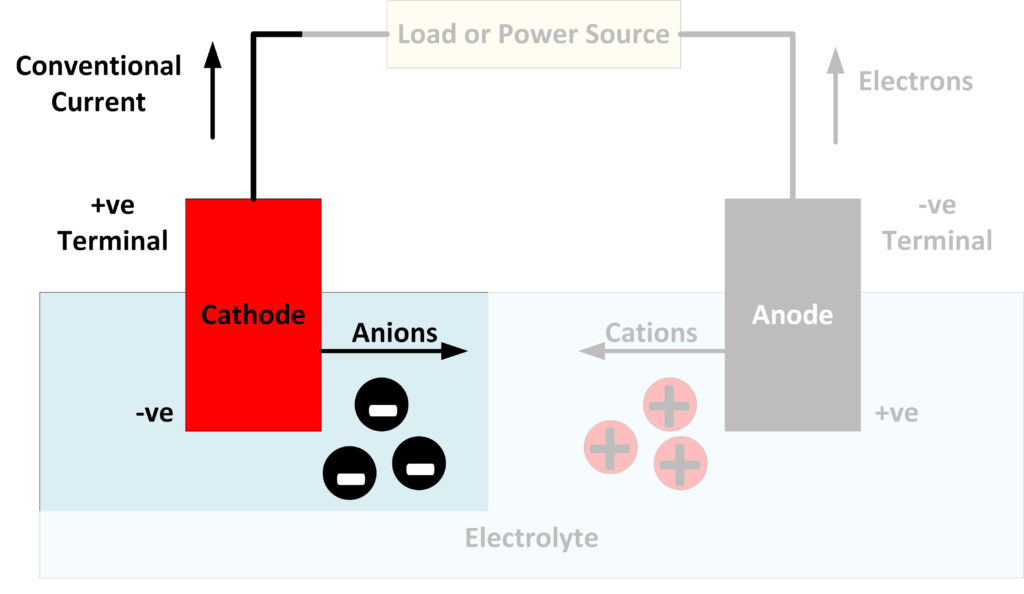
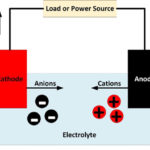
A cathode is an electrode where reduction reactions occur, in which atoms gain electrons. Negatively charged free electrons flow into the positive terminal of a battery as an electrical current. Because electrons are negatively charged, electricity is conventionally considered to flow in the opposite direction to the flow of electrons. Cations, positively charged atoms which have lost electrons, flow towards the cathode. In a battery or fuel cell, they flow through the electrolyte. Anions, negatively charged atoms with excess electrons, are produced at the cathode and flow towards the anode.
The cathode is attached to the battery’s positive terminal, but the cathode is itself polarized, with its negative end in contact with the electrolyte inside the battery. The cathode, therefore, attracts the positively charged cations.
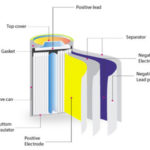
Cathodes are one of the key components of batteries, fuel cells, and other polarized electrical devices such as vacuum tubes. Although technically, a cathode is defined as an electrode where reduction reactions occur, with atoms gaining electrons, in a rechargeable battery, this process reverses. It is, therefore, common to always refer to the cathode as the electrode which acts as a cathode during battery discharge. In reality, this electrode becomes an anode during charging, when the flow of current reverses, but generally, it continues to be referred to as the cathode.
Cathode chemistry has been key to the development of lithium-ion batteries. For this reason, different battery technologies are often named for the materials used in their cathodes. Some examples of lithium-ion technologies include:
- NMC uses a lithium, nickel, manganese, and cobalt oxide cathode.
- LMO uses a lithium manganese oxide cathode.
- LFP uses a lithium iron phosphate cathode.
There is some concern that there may now be limited scope for further optimization of cathode chemistry in lithium-ion batteries. Research efforts are therefore turning to alternative anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and entirely new battery chemistries such as aluminum-ion batteries.


Tell Us What You Think!