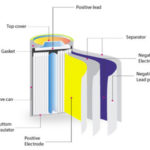
In simple terms, cell potential is the voltage of a single electrochemical cell. A battery may package a number of cells in series in order to increase the voltage of the battery. Cell potential is inherent in a particular chemical reaction, so a fully charged lead-acid battery will always have cell potentials of approximately 2.1 V, regardless of the size of the battery. Similarly, lithium-ion batteries have nominal cell potentials of between 3.2 and 3.85 V depending on the cathode material. The actual electric potential of a cell depends on temperature, concentration, and pressure.
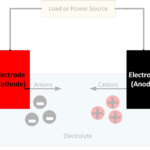
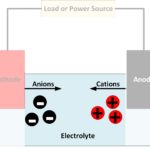
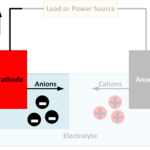
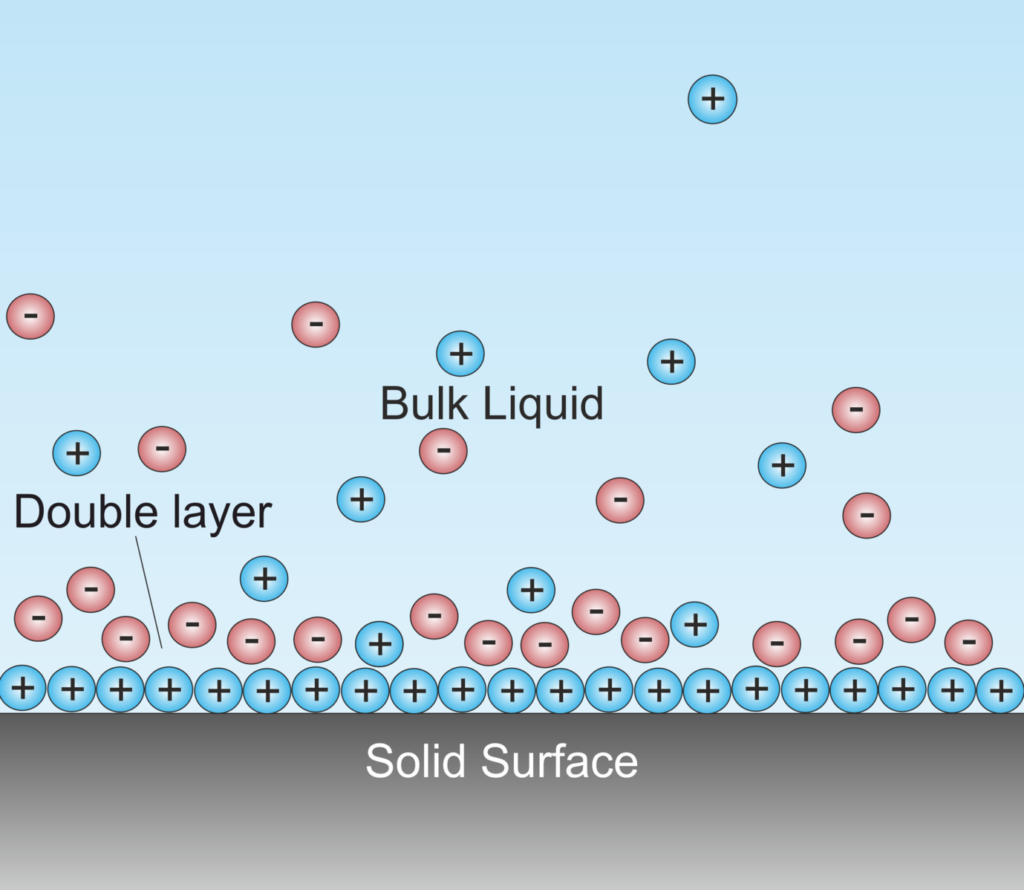 A battery converts chemically stored energy into electrical energy by redox reactions. This involves two half-reactions, with oxidation taking place at the anode and reduction occurring at the cathode. A half-cell is one of the electrodes and the electrolyte immediately surrounding it, which forms an electrical double layer (EDL) made up of pairs of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
A battery converts chemically stored energy into electrical energy by redox reactions. This involves two half-reactions, with oxidation taking place at the anode and reduction occurring at the cathode. A half-cell is one of the electrodes and the electrolyte immediately surrounding it, which forms an electrical double layer (EDL) made up of pairs of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
For a real electrochemical cell, the electric potential across the terminals can be directly measured in volts. The potential for each half-cell cannot be measured within a complete electrochemical cell. When calculating the theoretical potential of a battery, perhaps during design, it is necessary to consider the reactions for each half-cell. It is also possible to measure half cell potentials by pairing a half-cell with the standard hydrogen electrode which serves as a reference electrode.
The current flowing through an electrochemical cell is related to the Gibbs free energy change for the cell reaction. This is a product of the number of electrons transferred per unit of the overall reaction, the cell potential in volts, and the Faraday constant (96 485 C/mol). The theoretical cell potential depends on the composition of the reaction mixture and can be calculated using the Nernst equation.

Tell Us What You Think!