Littelfuse, Inc. announced the new ITV4030, a series of 22 amp, three-terminal, surface-mountable Li-ion battery protectors. These 4.0 x 3.0 mm devices protect battery packs against overcurrent and overcharging (overvoltage) conditions. The innovative design uses embedded fuse and heater elements that provide fast response and reliable performance to interrupt the charging or discharging circuit before the […]
Li-ion battery protectors prevent overcharging, overcurrent damage
Littelfuse, Inc. announced the new ITV4030, a series of 22 amp, three-terminal, surface-mountable Li-ion battery protectors. These 4.0 x 3.0 mm devices protect battery packs against overcurrent and overcharging (overvoltage) conditions. The innovative design uses embedded fuse and heater elements that provide fast response and reliable performance to interrupt the charging or discharging circuit before the […]
Li-ion batteries, Part 5: electrolytes
The electrolyte is often an underappreciated component in Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. They simply provide an electrical path between the anode and cathode that supports current (actually, ion) flow. But electrolytes are a key to battery performance, and advances in electrolyte chemistries are expected to be an important development leading to high-performance, safe, and low-cost Li-ions…
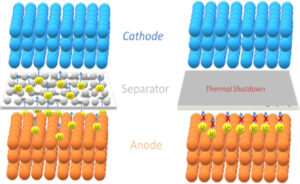
Li-ion batteries, Part 4: separators
Separators in Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries literally separate the anode and cathode to prevent a short circuit. Modern separator technology also contributes to a cell’s thermal stability and safety. Separators impact several battery performance parameters, including cycle life, energy and power density, and safety. The separator increases internal cell resistance, and the separator takes up valuable…
Li-ion batteries, Part 3: anodes
There are numerous cathode materials used in Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries optimized for various aspects of performance, but the majority of all Li-ions still use graphite anodes. That may be set to change. The use of graphite with a theoretical gravimetric capacity of about 370mAh/g is being challenged by new materials under development that offer gravimetric…
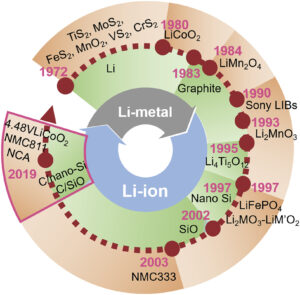
Li-ion batteries, Part 2: cathodes
Among the various components involved in a lithium-ion cell, cathodes (the positive or oxidizing electrodes) currently limit the energy density and dominate the battery cost. Today’s common cobalt (Co) and manganese (Mn) based cathodes were developed to overcome safety concerns with Li-metal anodes. This FAQ begins with a brief look at the longer-term trajectory of…
Li-ion batteries: building massless batteries
Battery cells, modules, and systems support many electronic, transportation, and energy applications. This article briefly reviews the operation of rechargeable batteries and looks at the energy storage value chain; it then presents common battery cell formats and how battery cells are assembled into modules and systems, reviews the development of multi-function structural battery packs, and…
Basics of zinc-ion batteries
By Ryan Brown, co-founder and CEO, Salient Energy Lithium-ion batteries are the leading battery technology for both electric vehicles (EVs) and the renewable energy industry. This makes it critical in the fight against climate change, with the world’s ability to adopt EVs and renewables limited in part by its ability to source lithium-ion raw materials. This…
New technique extends lithium-metal battery life
Examine a toy with a rechargeable battery and you are likely to find a lithium-polymer cell powering the works. But a new kind of battery architecture called lithium-metal is getting a lot of attention these days because it has a capacity and energy density potentially far exceeding that of lithium-polymer versions. Lithium-metal batteries use lithium…
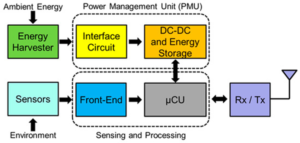
Don’t rush to choose rechargeable batteries…at least, not yet
Using energy harvesting and a rechargeable battery to power a remote wireless IoT node seems like an obvious and straightforward solution, but there are some unique aspects to consider. Don’t get me wrong: I really like rechargeable batteries; in fact, I like them a lot. Whether based on lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, lithium-ion, or other chemistry, our […]