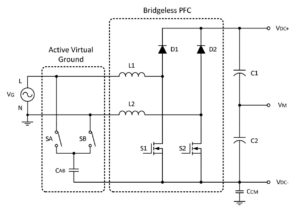
Rail splitters are usually associated with battery-powered devices, but that’s not always the case. There are several definitions of a “rail splitter,” sometimes referred to as a “virtual ground” or “pseudo ground.” The most common meaning is creating a new “0V” reference point, usually the mid-point Vin/2 of a single supply voltage such as a […]
Battery safety standards and testing
Lithium-ion battery (LIB) safety is a major concern for designers. LIBs are generally safe to use if they have been properly manufactured and are integrated correctly into systems. However, the use of sub-standard materials and the possibility of manufacturing or design defects can result in hazardous conditions. As a result, there are many global safety […]
Solid-state EV batteries – are we there yet?
The short answer is ‘no.’ We might be getting closer, but there’s still no guarantee that we’ll get there soon. Some automakers are looking at 2024 for the introduction of solid-state batteries in EVs, but others don’t see that happening until 2030. Expectations are high but unfulfilled. This FAQ reviews the anticipated benefits of solid-state…
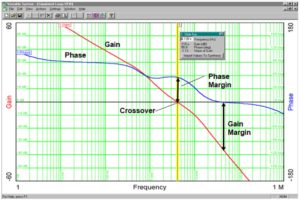
Bode plots and power supplies
A Bode plot represents the gain and phase of a feedback system as a function of frequency. It was developed by Hendrik Wade Bode in the 1930s and reflected the frequency domain behavior of a system. He invented it while at Bell Labs to help design stable amplifiers with the feedback needed in telephone networks.…
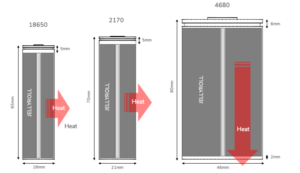
18650, 21700, 30700, 4680 and other Li-ions – what’s the difference?
There are many sizes of cylindrical lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells, and the number of sizes continues to grow. Some are optimized for use in simple devices such as toys and flashlights; others are mainly found powering portable electronics and electric vehicles. This FAQ begins by reviewing the broad landscape of cylindrical Li-ions, including protected and non-protected…
EV battery thermal management challenges
Keeping EV batteries cooled is the most common thermal management concern. However, batteries used in cold climates often benefit from being heated when temperatures fall. When undergoing fast charging or extra fast charging (XFC) batteries may need additional levels of cooling. This FAQ first considers various active and passive cooling technologies for EV batteries. It…
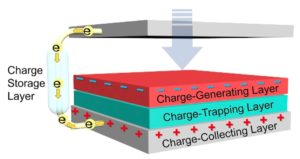
What are TENGs and PENGs and what are they good for?
Small self-powered systems, including wireless sensors and small robots currently under development, can use triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) and piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) as prime power sources. TENGs and PENGs offer large open circuit voltages, low materials cost, ease of fabrication, and good energy conversion efficiencies. TENGs use triboelectricity, commonly called static electricity, to convert common mechanical […]
What are the applications of 3D and 4D printed electronics?
3D printing is the fabrication of a three-dimensional object under computer control, with one or more materials being added layer by layer. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is used across various electronics applications, including circuit boards, energy storage devices, actuators, and sensors. It can be implemented using a variety of technologies, including selective laser sintering […]
The difference between primary and secondary battery chemistries
There are several differences between primary and secondary batteries. The most obvious is that primary batteries are single-use devices while secondary batteries can be recharged and used many times, but that’s not the only difference. This FAQ starts with a general overview of the differences between primary and secondary batteries; it will then look at…
How to read battery discharge curves
Batteries are complex electrochemical and thermodynamic systems, and multiple factors impact battery performance. Of course, battery chemistry is at the top of the list. Still, factors such as charge and discharge rates, operating temperatures, storage conditions, physical construction details, and more come into play when understanding which battery best suits a specific application. To begin,…