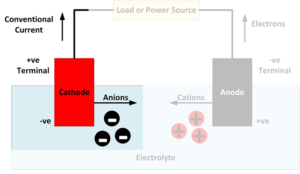
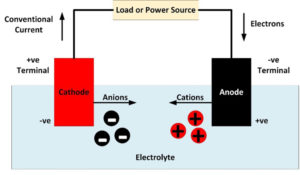
An anode is an electrode where oxidation reactions occur, involving atoms giving up electrons. The negatively charged free electrons then flow out of the negative terminal of the battery to produce an electrical current. It should be noted that conventionally, electricity is considered to flow in the opposite direction to the flow of electrons. Anions,…
What is a cathode?
A cathode is an electrode where reduction reactions occur, in which atoms gain electrons. Negatively charged free electrons flow into the positive terminal of a battery as an electrical current. Because electrons are negatively charged, electricity is conventionally considered to flow in the opposite direction to the flow of electrons. Cations, positively charged atoms which…
Understanding battery terminology
When discussing batteries, a lot of technical terms are used. If you’re not familiar with these terms, it can be challenging to understand a discussion of battery technology. This page lists some of the most important battery-related terms: Conventional Current: Electricity is conventionally considered to flow from positive to negative. However, because electrons are negatively…
What is a battery?
A battery comprises several voltaic cells – electrochemical cells that generate electrical energy from chemical reactions. The cells in a battery have their own self-contained source of chemical energy, unlike a fuel cell which is powered by an external supply of chemicals. Electricity is the flow of electrons, and the chemical reactions in batteries involve…